Organizations managing sensitive applications must ensure secure communication to maintain data privacy, even within internal services. Achieving end-to-end encryption on Amazon EKS in a Kubernetes environment comes with its own set of challenges:
Key Challenges:
- Certificate Management Complexity: Managing certificates for every microservice in a distributed architecture can become a daunting task.
- Ingress Limitations: Kubernetes ingress backed by a Network Load Balancer (NLB) lacks native support for client certificates.
- Manual Certificate Rotation: Regularly rotating certificates manually increases administrative overhead.
- Mutual TLS Constraints: Standard Kubernetes ingress configurations do not support mutual TLS out of the box.
The Solution:
By leveraging the NGINX Ingress Controller on Amazon EKS, organizations can implement mutual TLS. Additionally, integrating cert-manager with Let’s Encrypt simplifies certificate provisioning and automates certificate rotation. This approach enhances both security and compliance, meeting the stringent requirements of organizations with sensitive workloads.
Target Architecture (end-to-end encryption on Amazon EKS)
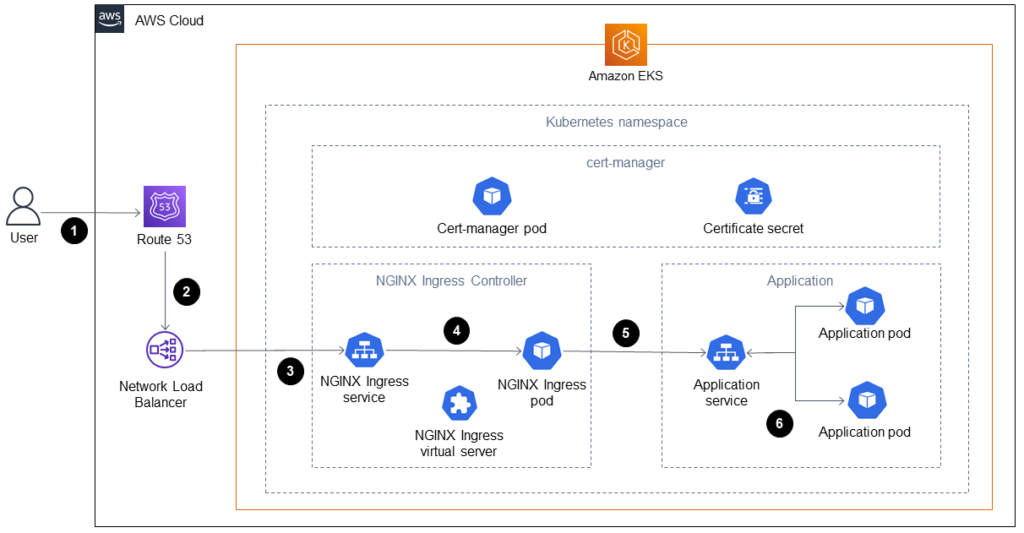
Reference: [AWS White Papers]
The diagram shows how the end-to-end encryption workflow operates:
- A client sends a request to access the application to the DNS name.
- The Route 53 record is a CNAME to the Network Load Balancer.
- The Network Load Balancer forwards the request to the NGINX Ingress Controller that is configured with a TLS listener. Communication between the NGINX Ingress Controller and the Network Load Balancer follows HTTPS protocol.
- The NGINX Ingress Controller carries out path-based routing based on the client’s request to the application service.
- The application service forwards the request to the application pod. The application is designed to use the same certificate by calling secrets.
- Pods run the sample application using the cert-manager certificates. The communication between the NGINX Ingress Controller and the pods uses HTTPS.
Cert-manager Highlights
- Namespace Isolation:
Cert-manager operates in its dedicated namespace, maintaining isolation and simplifying management. - Certificate Provisioning:
Certificates are issued as secrets within the namespaces where they are needed. These secrets can then be linked to:- Application Pods
- NGINX Ingress Controller
- Automation:
Cert-manager automates the provisioning and rotation of certificates, reducing administrative overhead while maintaining a robust security posture.
Why End-to-End Encryption Matters
Securing service-to-service communication with end-to-end encryption isn’t just a best practice—it’s essential for maintaining:
- Data Integrity: Protecting sensitive information in transit.
- Trust: Ensuring that internal and external stakeholders can rely on the security of your microservices architecture.
With the combination of Amazon EKS, NGINX Ingress Controller, and cert-manager, organizations can achieve seamless, automated, and robust end-to-end encryption that scales with their needs.
Refer to the link for detailed insights.
